@hex-engine/2d
@hex-engine/2d is the main package that you will interact with when using Hex Engine. It has several named exports, which are each documented here.
NOTE:
@hex-engine/2dalso re-exports everything from@hex-engine/core, but those exports are not documented here. Check the API documentation for@hex-engine/coreif you can't find what you're looking for here.
Models
@hex-engine/2d includes several "Models", which are classes representing common data structures that are used throughout the library.
Circle
Available since version: 0.0.1
import { Circle } from "@hex-engine/2d";
Represents a circle; a shape with infinite points along its edge that are all equidistant from its center.
The distance between the center and the edge points is known as the circle's radius.
Static Methods
constructor
Available since version: 0.0.1
constructor(radius: number)
Creates a new Circle.
Properties
radius
Available since version: 0.0.1
radius: number
The radius of this circle; the length of a line segment that starts at the circle's center and goes to its edge.
This property is readonly in versions prior to 0.1.0.
diameter
Available since version: 0.0.1
diameter: number
The diameter of this circle; the length of a line segment that starts at the circle's edge, crosses through the circle's center, and continues to the opposite edge.
This property is readonly in versions prior to 0.1.0.
width
Available since version: 0.0.1
width: number
The width of this circle; same as the diameter.
This property is readonly in versions prior to 0.1.0.
height
Available since version: 0.0.1
height: number
The height of this circle; same as the diameter.
This property is readonly in versions prior to 0.1.0.
Methods
boundingRectangle
Available since version: 0.0.1
boundingRectangle(): Polygon
Creates a rectangular polygon whose width and height are double this circle's radius; said in other words, returns the rectangle that this circle could be perfectly inscribed in.
containsPoint
Available since version: 0.0.1
containsPoint(point: Vector): boolean
Returns a value indicating if a given point is either within the circle or on the its edge.
equals
Available since version: 0.0.1
equals(other: Circle): boolean
Returns whether this circle has the same radius as another.
draw
Available since version: 0.0.1
draw(context: CanvasRenderingContext2D, strokeOrFill: "stroke" | "fill", { x = 0, y = 0 }: { x?: number | undefined; y?: number | undefined } = {}): void
Draws this circle onto a canvas context, using the current stroke or fill style.
Grid
Available since version: 0.0.0
class Grid<T>
import { Grid } from "@hex-engine/2d";
Represents a two-dimensional Grid with arbitrary contents in each cell.
Static Methods
constructor
Available since version: 0.0.0
constructor(rows: number, columns: number, defaultValue: T)
constructor(rowsAndCols: Vector, defaultValue: T)
Creates a new Grid.
Properties
size
Available since version: 0.0.0
size: Vector
The size of the grid, in rows and columns.
defaultValue
Available since version: 0.0.0
defaultValue: T
The default value to initialize empty cells with.
Methods
setData
Available since version: 0.0.0
setData(data: Array<T>): void
Fill in the grid with the provided data, represented as a 2D array.
get
Available since version: 0.0.0
get(row: number, column: number): T
get(pos: Vector): T
Get the value in the cell at the given row and column index.
set
Available since version: 0.0.0
set(row: number, column: number, value: T): void
set(pos: Vector, value: T): void
Set the value in the cell at the given row and column index.
contents
Available since version: 0.0.0
*contents(): Generator<[number, number, T]>
Returns an iterable of all the contents of this grid and their row and column indices.
Vector
Available since version: 0.0.1
import { Vector } from "@hex-engine/2d";
A two-dimensional vector, used to represent points, sizes, and more.
In versions prior to 0.0.1, this class was called
Vec2. In versions >= 0.0.1 but prior to 0.2.0, this class was calledPoint.
Static Properties
ZERO
Available since version: 0.11.2
ZERO: Vector
A Vector with x and y of 0. Do NOT mutate this.
Static Methods
constructor
Available since version: 0.0.0
constructor(x: number, y: number)
Creates a new Vector.
from
Available since version: 0.0.1
static from({ x, y }: { x: number; y: number }): Vector
Create a Vector from any object with an x property and a y property.
fromAngleAndMagnitude
Available since version: 0.2.0
static fromAngleAndMagnitude(angle: number, magnitude: number): Vector
Create a Vector from an angle and magnitude.
Properties
x
Available since version: 0.0.0
x: number
y
Available since version: 0.0.0
y: number
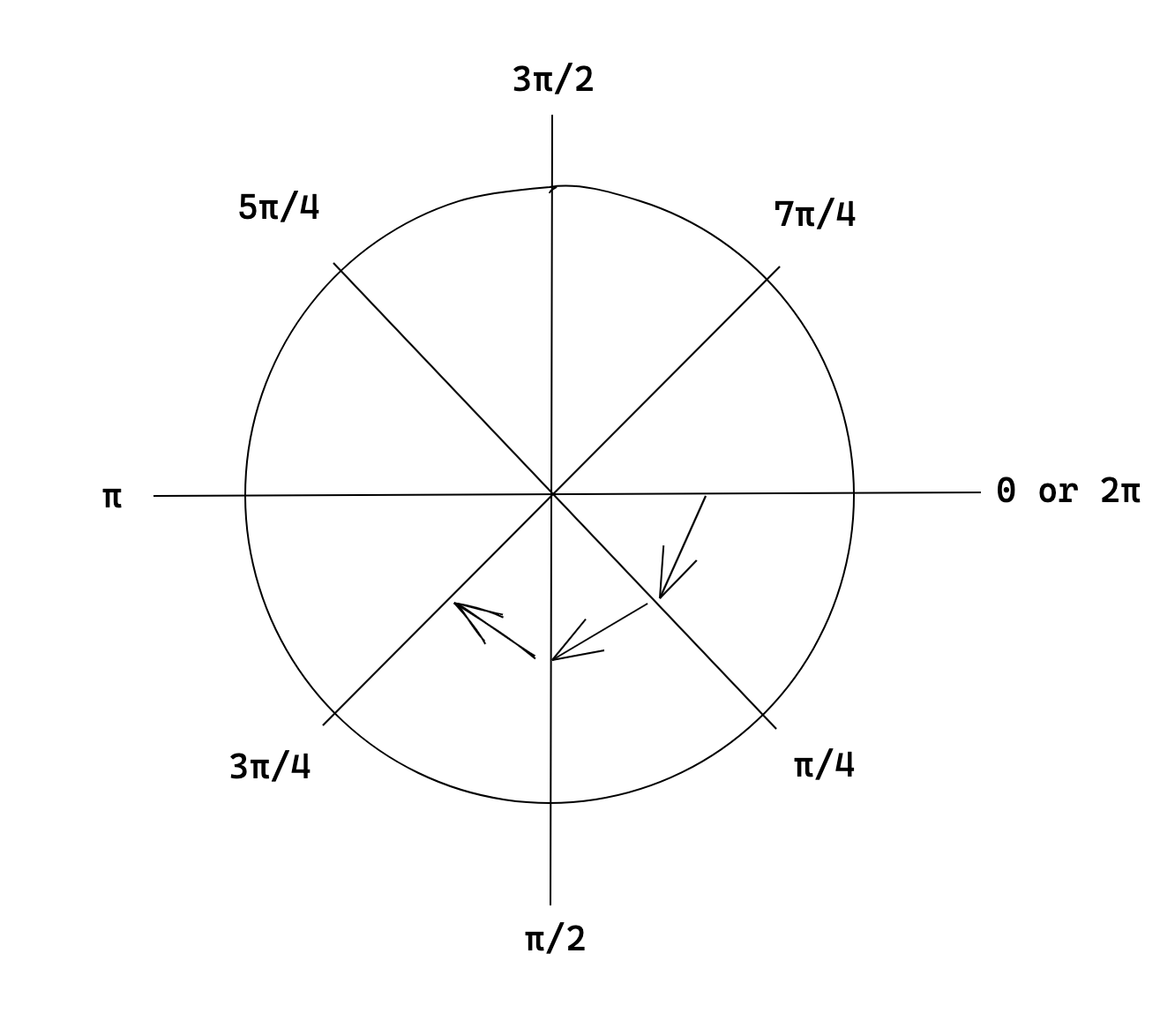
angle
Available since version: 0.2.0
angle: number
Angles are expressed as the clockwise distance from the x-axis. This is different from how angles are expressed in normal coordinate space; the reason for this difference is because when drawing to a canvas, the positive y axis points downwards instead of upwards.
magnitude
Available since version: 0.2.0
magnitude: number
The distance of the point (x, y) from the origin (0, 0).
Methods
clone
Available since version: 0.0.1
clone(): Vector
Create a new Vector with the same x and y values as this one.
opposite
Available since version: 0.0.1
opposite(): Vector
Create a new Vector whose x and y values have the opposite sign as this one's.
oppositeMutate
Available since version: 0.0.1
oppositeMutate(): this
Mutate this Vector so that its x and y values have the opposite sign.
add
Available since version: 0.0.0
add(other: Vector | number): Vector
Create a new Vector whose x and y values are equivalent to this one's, but with the specified value added.
addMutate
Available since version: 0.0.0
addMutate(other: Vector | number): this
Mutate this Vector by adding the specified value to its x and y values.
addX
Available since version: 0.0.1
addX(amount: number): Vector
Create a new Vector whose x and y values are equivalent to this one's, but with the specified value added to the x value.
addXMutate
Available since version: 0.0.1
addXMutate(amount: number): this
Mutate this Vector by adding the specified value to its x value.
addY
Available since version: 0.0.1
addY(amount: number): Vector
Create a new Vector whose x and y values are equivalent to this one's, but with the specified value added to the y value.
addYMutate
Available since version: 0.0.1
addYMutate(amount: number): this
Mutate this Vector by adding the specified value to its y value.
subtract
Available since version: 0.0.0
subtract(other: Vector | number): Vector
Create a new Vector whose x and y values are equivalent to this one's, but with the specified value subtracted.
subtractMutate
Available since version: 0.0.0
subtractMutate(other: Vector | number): this
Mutate this Vector by subtracting the specified value from its x and y values.
subtractX
Available since version: 0.0.1
subtractX(amount: number): Vector
Create a new Vector whose x and y values are equivalent to this one's, but with the specified value subtracted from the x value.
subtractXMutate
Available since version: 0.0.1
subtractXMutate(amount: number): this
Mutate this Vector by subtracting the specified value from its x value.
subtractY
Available since version: 0.0.1
subtractY(amount: number): Vector
Create a new Vector whose x and y values are equivalent to this one's, but with the specified value subtracted from the y value.
subtractYMutate
Available since version: 0.0.1
subtractYMutate(amount: number): this
Mutate this Vector by subtracting the specified value from its y value.
multiply
Available since version: 0.0.0
multiply(other: Vector | number): Vector
Create a new Vector whose x and y values are equivalent to this one's, but with each multiplied by the specified value.
In versions prior to 0.0.1, this method was named
times.
multiplyMutate
Available since version: 0.0.0
multiplyMutate(other: Vector | number): this
Mutate this Vector by multiplying its x and y values with the specified value.
In versions prior to 0.0.1, this method was named
timesMutate.
multiplyX
Available since version: 0.0.1
multiplyX(amount: number): Vector
Create a new Vector whose x and y values are equivalent to this one's, but with the x value multiplied by the specified value.
multiplyXMutate
Available since version: 0.0.1
multiplyXMutate(amount: number): this
Mutate this Vector by multiplying its x value by the specified value.
multiplyY
Available since version: 0.0.1
multiplyY(amount: number): Vector
Create a new Vector whose x and y values are equivalent to this one's, but with the y value multiplied by the specified value.
multiplyYMutate
Available since version: 0.0.1
multiplyYMutate(amount: number): this
Mutate this Vector by multiplying its y value by the specified value.
divide
Available since version: 0.0.0
divide(other: Vector | number): Vector
Create a new Vector whose x and y values are equivalent to this one's, but with each divided by the specified value.
In versions prior to 0.0.1, this method was named
dividedBy.
divideMutate
Available since version: 0.0.0
divideMutate(other: Vector | number): this
Mutate this Vector by dividing its x and y values by the specified value.
In versions prior to 0.0.1, this method was named
dividedByMutate.
divideX
Available since version: 0.0.1
divideX(amount: number): Vector
Create a new Vector whose x and y values are equivalent to this one's, but with its x value divided by the specified value.
divideXMutate
Available since version: 0.0.1
divideXMutate(amount: number): this
Mutate this Vector by dividing its x value by the specified value.
divideY
Available since version: 0.0.1
divideY(amount: number): Vector
Create a new Vector whose x and y values are equivalent to this one's, but with its y value divided by the specified value.
divideYMutate
Available since version: 0.0.1
divideYMutate(amount: number): this
Mutate this Vector by dividing its y value by the specified value.
equals
Available since version: 0.0.0
equals(other: Vector): boolean
Check if this Vector and another Vector have the same x and y values.
distanceTo
Available since version: 0.0.0
distanceTo(other: Vector): number
Measure the distance between this Vector and another Vector.
round
Available since version: 0.0.0
round(): Vector
Return a new Vector that is the same as this Vector, but with its x and y values rounded to the nearest integer.
roundMutate
Available since version: 0.0.0
roundMutate(): this
Mutate this Vector by rounding its x and y values to the nearest integer.
roundDown
Available since version: 0.0.0
roundDown(): Vector
Return a new Vector that is the same as this Vector, but with its x and y values rounded down to the nearest integer.
roundDownMutate
Available since version: 0.0.0
roundDownMutate(): this
Mutate this Vector by rounding its x and y values down to the nearest integer.
roundUp
Available since version: 0.0.0
roundUp(): Vector
Return a new Vector that is the same as this Vector, but with its x and y values rounded up to the nearest integer.
roundUpMutate
Available since version: 0.0.0
roundUpMutate(): this
Mutate this Vector by rounding its x and y values up to the nearest integer.
mutateInto
Available since version: 0.0.0
mutateInto(other: { x: number; y: number })
Mutate this Vector by setting its x and y values to the values found on the provided object.
In versions prior to 0.0.1, this method only accepted other Vector instances (though they were called Vec2 instances back then).
normalize
Available since version: 0.2.0
normalize(): Vector
Create a new Vector by normalizing the magnitude of this one (setting it to 1).
normalizeMutate
Available since version: 0.2.0
normalizeMutate(): this
Mutate this point by normalizing its magnitude (setting it to 1).
rotate
Available since version: 0.2.0
rotate(radians: number): Vector
Create a new Vector equivalent to this one but rotated by the specified amount (in radians), clockwise.
rotateMutate
Available since version: 0.2.0
rotateMutate(radians: number): this
Mutate this Vector by rotating it the specified amount (in radians), clockwise.
dotProduct
Available since version: 0.5.0
dotProduct(other: Vector): number
Returns the dot product of this vector with other. The resulting number is negative if the vectors face
opposite directions, and 0 if they are perpendicular.
perpendicular
Available since version: 0.5.0
perpendicular(): Vector
Returns a vector perpendicular to this vector, with the same magnitude.
perpendicularMutate
Available since version: 0.5.0
perpendicularMutate(): this
Rotate this vector to make it perpendicular to its former self.
asDOMPoint
Available since version: 0.0.0
asDOMPoint(): DOMPoint
Create a DOMPoint with the same x and y values as this Vector.
transformUsingMatrix
Available since version: 0.0.0
transformUsingMatrix(matrix: DOMMatrix): Vector
Create a new Vector by transforming this Vector using the provided DOMMatrix.
transformUsingMatrixMutate
Available since version: 0.0.0
transformUsingMatrixMutate(matrix: DOMMatrix): this
Mutate this Vector by transforming its x and y values using the provided DOMMatrix.
ReadOnlyVector
Available since version: 0.9.0
import { ReadOnlyVector } from "@hex-engine/2d";
A TypeScript interface representing a Vector instance with all its writable properties and mutating methods removed.
If you want to provide a Vector to other parts of the code but do not want it to be mutated, you can use this interface.
Note that even though it's called ReadOnlyVector, the real underlying instance at runtime is still a normal, mutable Vector. This is just a TypeScript interface intended for documentation/warning purposes so that consumers can understand whether they are allowed to mutate a received Vector or not.
Polygon
Available since version: 0.0.1
import { Polygon } from "@hex-engine/2d";
Represents a closed shape consisting of a set of connected straight line segments.
Static Methods
constructor
Available since version: 0.0.1
constructor(points: Array<Vector>)
Creates a new Polygon.
The points are ordered such that one could draw the polygon by placing a pen down at the first point, then dragging the pen in a straight line to the second point, then the third, and so on until the last point, which is connected to the first point.
Note that the x and y values on the points on the created Polygon may not be the same as the x and y values on the points you give here, because the constructor calculates the centroid of the polygon and then recenters all points around it.
rectangle
Available since version: 0.0.1
static rectangle(size: Vector): Polygon
static rectangle(width: number, height: number): Polygon
Creates a rectangular polygon; a 4-sided polygon where the angles between all sides are all π/2 radians (90 degrees).
Properties
points
Available since version: 0.0.1
points: Array<Vector>
Points representing the corners where the polygon's line segments meet.
Their x and y properties refer to their position relative to the
polygon's centroid.
The points are ordered such that one could draw the polygon by placing a pen down at the first point, then dragging the pen in a straight line to the second point, then the third, and so on until the last point, which is connected to the first point.
This property is readonly in versions prior to 0.1.0.
width
Available since version: 0.0.1
width: number
The horizontal distance between the leftmost point in the polygon and the rightmost point on the polygon.
This property is readonly in versions prior to 0.1.0.
height
Available since version: 0.0.1
height: number
The vertical distance between the highest point in the polygon and the lowest point on the polygon.
This property is readonly in versions prior to 0.1.0.
Methods
boundingRectangle
Available since version: 0.0.1
boundingRectangle(): Polygon
Creates a rectangular polygon whose width and height match that of this polygon; said in other words, returns the rectangle that this polygon could be perfectly inscribed in.
containsPoint
Available since version: 0.0.1
containsPoint(point: Vector): boolean
Returns whether the given point falls inside the polygon.
equals
Available since version: 0.0.1
equals(other: Polygon): boolean
Returns whether this polygon has the same point values as another.
draw
Available since version: 0.0.1
draw(context: CanvasRenderingContext2D, strokeOrFill: "stroke" | "fill", { x = 0, y = 0 }: { x?: number | undefined; y?: number | undefined } = {}): void
Draws this polygon onto a canvas context, using the current stroke or fill style.
TransformMatrix
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { TransformMatrix } from "@hex-engine/2d";
Static Properties
IDENTITY
Available since version: 0.11.2
IDENTITY: TransformMatrix
An identity TransformMatrix, ie. one that has no effect when applied. Do NOT mutate this.
Static Methods
constructor
Available since version: 0.0.0
constructor()
constructor(a: number, b: number, c: number, d: number, e: number, f: number)
Creats a new TransformMatrix. If no a-f values are provided, they will default to the identity matrix.
fromDOMMatrix
Available since version: 0.0.0
static fromDOMMatrix(domMatrix: DOMMatrix): TransformMatrix
Create a TransformMatrix from a DOMMatrix of SVGMatrix.
Properties
a
Available since version: 0.0.0
readonly a: number
Returns the a component of this TransformMatrix, where this TransformMatrix's components can be represented as follows:
[ a c e
b d f
0 0 1 ]
The a component affects horizontal scaling. A value of 1 results in no scaling.
b
Available since version: 0.0.0
readonly b: number
Returns the b component of this TransformMatrix, where this TransformMatrix's components can be represented as follows:
[ a c e
b d f
0 0 1 ]
The b component affects vertical skewing.
c
Available since version: 0.0.0
readonly c: number
Returns the c component of this TransformMatrix, where this TransformMatrix's components can be represented as follows:
[ a c e
b d f
0 0 1 ]
The c component affects horizontal skewing.
d
Available since version: 0.0.0
readonly d: number
Returns the d component of this TransformMatrix, where this TransformMatrix's components can be represented as follows:
[ a c e
b d f
0 0 1 ]
The d component affects vertical scaling. A value of 1 results in no scaling.
e
Available since version: 0.0.0
readonly e: number
Returns the e component of this TransformMatrix, where this TransformMatrix's components can be represented as follows:
[ a c e
b d f
0 0 1 ]
The e component affects horizontal translation (movement).
f
Available since version: 0.0.0
readonly f: number
Returns the f component of this TransformMatrix, where this TransformMatrix's components can be represented as follows:
[ a c e
b d f
0 0 1 ]
The f component affects vertical translation (movement).
Methods
scale
Available since version: 0.0.0
scale(size: Vector, origin: Vector): TransformMatrix
scale(sizeX: number, sizeY: number, originX: number, originY: number): TransformMatrix
Creates a new TransformMatrix with the same values as this one, but with a scale operation applied.
scaleMutate
Available since version: 0.0.0
scaleMutate(size: Vector, origin: Vector): this
scaleMutate(sizeX: number, sizeY: number, originX: number, originY: number): this
Mutates this TransformMatrix by applying a scale operation.
translate
Available since version: 0.0.0
translate(pos: Vector): TransformMatrix
translate(x: number, y: number): TransformMatrix
Creates a new TransformMatrix with the same values as this one, but with a translation applied.
translateMutate
Available since version: 0.0.0
translateMutate(pos: Vector): this
translateMutate(x: number, y: number): this
Mutates this TransformMatrix by applying a translation.
rotate
Available since version: 0.0.0
rotate(radians: number): TransformMatrix
Creates a new TransformMatrix with the same values as this one, but with a rotation applied.
rotateMutate
Available since version: 0.0.0
rotateMutate(radians: number): this
Mutates this TransformMatrix by applying a rotation.
multiply
Available since version: 0.0.0
multiply(other: TransformMatrix | DOMMatrix): TransformMatrix
Creates a new TransformMatrix by multiplying this one with another.
In versions prior to 0.0.1, this method is called
times.
multiplyMutate
Available since version: 0.0.0
multiplyMutate(other: TransformMatrix | DOMMatrix): this
Mutates this TransformMatrix by multiplying it with another.
In versions prior to 0.0.1, this method is called
timesMutate.
transformPoint
Available since version: 0.0.0
transformPoint(point: Vector): Vector
Applies this TransformMatrix's transform to the provided Vector values, and returns a new Vector.
This does not mutate the provided Vector.
transformPointMutate
Available since version: 0.1.0
transformPointMutate(point: Vector): Vector
Applies this TransformMatrix's transform to the provided Vector values, and mutates the provided Vector to contain the transformed values.
inverse
Available since version: 0.0.0
inverse(): TransformMatrix
Return a new TransformMatrix that applies the inverse transformation as this one.
inverseMutate
Available since version: 0.0.0
inverseMutate(): this
Mutate this TransformMatrix by inverting its transformation.
AnimationFrame
Available since version: 0.0.0
class AnimationFrame<T>
import { AnimationFrame } from "@hex-engine/2d";
A class that represents a single frame in an animation.
The data that is in this frame can be anything.
Static Methods
constructor
Available since version: 0.0.0
constructor(data: T, { duration, onFrame }: { duration: number; onFrame?: null | (() => void) })
Creates a new AnimationFrame.
Properites
data
Available since version: 0.0.0
data: T
The data contained in this frame.
duration
Available since version: 0.0.0
duration: number // in ms
The duration of this frame, in milliseconds.
onFrame
Available since version: 0.0.0
onFrame: (() => void) | null
A function to call when this frame is reached; can be used, for example, to play sound effects.
HexMouseEvent
Available since version: 0.0.1
import { HexMouseEvent } from "@hex-engine/2d";
A Mouse event in Hex Engine.
You will almost never construct this class manually; instead, an instance of it will be passed to listener functions you set up using the Mouse or LowLevelMouse components.
Properties
pos
Available since version: 0.0.1
pos: Vector
The position of the cursor, relative to the current Entity's origin.
delta
Available since version: 0.0.1
delta: Vector
The amount that the cursor has moved since the last frame.
buttons
Available since version: 0.0.1
buttons: { left: boolean, right: boolean, middle: boolean, mouse4: boolean, mouse5: boolean }
Which buttons were pressed during this event, or, in the case of a MouseUp event, which buttons were released.
Components
@hex-engine/2d includes several Component functions that you can use in your Entities.
Canvas
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { Canvas } from "@hex-engine/2d";
The built-in Canvas component that should be placed on your root Entity in order to render everything in your game.
function Canvas(options: {
/**
* You can specify an existing Canvas element to render into, if desired.
* If you do not, one will be created.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
element?: HTMLCanvasElement;
/**
* The background color to set the canvas to prior to drawing each frame.
* If you pass `null`, the canvas will not be cleared prior to drawing each frame.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
* `null` supported since version: 0.9.0
*/
backgroundColor: string | null;
}): {
/**
* The canvas element; either the one you passed in,
* or one that was created, if you didn't pass one in.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
element: HTMLCanvasElement;
/**
* The canvas rendering context, as returned by `useContext`.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
context: CanvasRenderingContext2D;
/**
* Sets how the contents of the canvas should be scaled when
* the canvas width and height does not exactly match the screen
* output width and height. If you pass `true` to this function,
* nearest-neighbor scaling will be used (if supported by your browser).
* Otherwise, linear scaling will be used (or maybe bilinear or trilinear,
* depending on the browser).
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
setPixelated: (on: boolean) => void;
/**
* Resizes the canvas to the CSS sizes specified by `realWidth` and `realHeight`,
* and sets its internal render width and height to the amounts specified by
* `pixelWidth` and `pixelHeight`.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
resize(opts: {
realWidth: number | string;
realHeight: number | string;
pixelWidth: number;
pixelHeight: number;
}): void;
/**
* Resizes the canvas so that it takes up the entire window,
* and sets up a window resize listener that resize the canvas
* such that it is always a direct scale factor of the window size,
* based on the provided pixelZoom option.
*
* Note that the window resize listener created by this method cannot be removed;
* if you need more fine-grained control than what this method provides, use
* `useWindowSize` and the `resize` method on Canvas to set up your own listener.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
fullscreen({ pixelZoom?: number } = {}): void;
};
Canvas.DrawOrder
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { Canvas } from "@hex-engine/2d";
Canvas.DrawOrder;
This Component can be placed on the root Entity to specify the draw order that the
Canvas Component will use. If no Canvas.DrawOrder Component is present on the
root Entity, then Canvas.DrawOrder.defaultSort will be used as the sort order.
function DrawOrder(
sort: (entities: Array<Entity>) => Array<Component>
): {
sort: (entities: Array<Entity>) => Array<Component>;
};
Animation
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { Animation, AnimationAPI } from "@hex-engine/2d";
A Component that represents an Animation, where each frame has a duration and contains arbitrary data.
function Animation<T>(
frames: Array<AnimationFrame<T>>,
options: { loop?: boolean | undefined }
): AnimationAPI<T>;
The
optionsparameter was added in version 0.1.3. Prior to version 0.1.3, all animations loop.
This Component function returns a type called AnimationAPI which is defined as follows:
type AnimationAPI<T> = {
/**
* The frames in the animation (as passed in).
*
* Available since version: 0.1.9
*/
readonly frames: Array<AnimationFrame<T>>;
/**
* Whether to loop the animation.
*
* Available since version: 0.1.9
*/
loop: boolean;
/**
* The index of the current frame within the frame array.
*
* Available since version: 0.1.9
*/
readonly currentFrameIndex: number;
/**
* The current animation frame; ie, current in time.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
readonly currentFrame: AnimationFrame<T>;
/**
* A number from 0 to 1 indicating how far we have gotten through the current frame.
*
* Available since version: 0.1.4
*/
readonly currentFrameCompletion: number;
/**
* Pause playback of this animation.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
pause(): void;
/**
* Resume playback of this animation.
*
* Available since version: 0.1.9
*/
resume(): void;
/**
* Begin playback of this animation.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
play(): void;
/**
* Restart playback of this animation from the first frame.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
restart(): void;
/**
* Go to a specific frame.
*
* Available since version: 0.1.10
*/
goToFrame(frameNumber: number): void;
};
AnimationSheet
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { AnimationSheet } from "@hex-engine/2d";
A Component representing an AnimationSheet image; that is, a filmstrip-style image of sprites which should be rendered in a particular sequence as part of an animation.
function AnimationSheet(options: {
url: string;
tileWidth: number;
tileHeight: number;
animations: {
[name: string]: AnimationAPI<number>;
};
}): {
/**
* The current animation, that frames will be drawn from.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
currentAnim: AnimationAPI<number>;
/**
* Draws the current frame of the current animation into the canvas.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*
* In versions prior to 0.0.1, this method was called `drawSpriteIntoContext`
* and had a different signature.
*/
draw(
context: CanvasRenderingContext2D,
options: {
x?: number | undefined;
y?: number | undefined;
width?: number | undefined;
height?: number | undefined;
} = {}
): void;
};
Aseprite
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { Aseprite } from "@hex-engine/2d";
import blueSlime from "./blueSlime.aseprite";
Aseprite(blueSlime);
A Component which loads and draws Aseprites sprites and animations.
function Aseprite(
data: AsepriteLoader.Data
): {
/**
* The current animation, that frames will be drawn from.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
currentAnim: AnimationAPI<HTMLCanvasElement>;
/**
* The aseprite-loader data that was passed into this function.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
data: AsepriteLoader.Data;
/**
* All the animations that were found in the Aseprite file.
*
* We use Tags to find these, and also include an animation called "default" which
* is the animation containing every frame in the file, in order.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
animations: {
[name: string]: AnimationAPI<HTMLCanvasElement>;
};
/**
* Draw the current animation frame into the provided canvas context.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*
* In versions prior to 0.0.1, this method was called `drawCurrentFrameIntoContext`
* and had a different signature.
*/
draw: (
context: CanvasRenderingContext2D,
options?: {
x?: number | undefined;
y?: number | undefined;
}
) => void;
/**
* The maximum size of the frames in this Aseprite file.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
size: Vector;
};
Audio
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { Audio } from "@hex-engine/2d";
A function that loads and plays a sound clip from a URL.
You can get a URL for a sound clip by importing it, as if it was code:
import mySound from "./my-sound.ogg";
console.log(typeof mySound); // "string"
useNewComponent(() => Audio({ url: mySound }));
When you import an audio clip in this way, it will be automatically added to the build and included in the final build output.
function Audio({
url,
}: Props): {
/**
* Play this audio clip, if it's loaded. If it isn't loaded yet, nothing will happen.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
play(options?: {
/**
* Specify the playback volume, from 0 to 1.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
volume?: number;
}): Promise<void>;
};
AudioContext
Available since version: 0.0.1
import { AudioContext } from "@hex-engine/2d";
A Component to be placed on the root Entity, which creates a Web Audio API
AudioContext upon first user interaction with the page.
Web browsers disallow playback of audio prior to user interaction, which is why this Component waits until the first click or keypress to come from the user before creating an AudioContext.
function AudioContextComponent(): {
/**
* The Web Audio API AudioContext instance, if it's been created yet.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
audioContext: AudioContext | null;
};
BMFont
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { BMFont } from "@hex-engine/2d";
import silver from "./silver.fnt";
BMFont(silver);
This Component uses an AngelCode BMFont-format file to render text into the canvas.
function BMFont(
data: BMFontLoader.Font
): {
/**
* The BMFont file data passed into this Component.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
data: BMFontLoader.Font;
/**
* All the Image Components that this Component created in order to load the font.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
images: Array<Image>;
/**
* Whether all the images the font references have been loaded yet.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
readyToDraw(): void;
/**
* Measures how many pixels wide the specified text would be,
* if it was rendered using this font.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
measureWidth(text: string): number;
/**
* Returns this font's size.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
getFontSize(): number;
/**
* Draws some text into the canvas, using this font.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*
* In versions prior to 0.0.1, this method had a different signature.
*/
drawText(
context: CanvasRenderingContext2D,
text: string,
options?: {
x?: number | undefined;
y?: number | undefined;
}
): void;
/**
* Measure the sizes of various aspects of this font.
* See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Typeface#Font_metrics
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
* Return value shape changed in version: 0.6.0
*/
measureText: (
text: string
) => {
/**
* The length of a vertical line drawn from the baseline to the mean line.
*
* In layman's terms: the height of lowercase letters like a, e, x, o, etc.
*
* Available since version: 0.6.0
*/
baselineToMeanLine: number;
/**
* The length of a vertical line drawn from the baseline to the cap line.
*
* In layman's terms: the height of uppercase letters.
*
* Available since version: 0.6.0
*/
baselineToCapLine: number;
/**
* The length of a vertical line drawn from the baseline to the descent line.
*
* In layman's terms: the height of the little tails that hang off the
* bottom of the baseline in lowercase letters like q, p, y, j, g, etc.
*
* Available since version: 0.6.0
*/
baselineToDescentLine: number;
/**
* The length of a vertical line drawn from the baseline to the ascent line.
*
* In layman's terms: the height of "tall" lowercase letters, like l, f, etc.
*
* Available since version: 0.6.0
*/
baselineToAscentLine: number;
/**
* The length of a vertical line drawn from the descent line to the ascent line.
*
* Available since version: 0.6.0
*/
descentLineToAscentLine: number;
/**
* The length of a vertical line drawn from the baseline to the bottom of
* Chinese, Japanese, and Korean characters.
*
* Available since version: 0.6.0
*/
baselineToCJKBottom: number;
/**
* The length of a vertical line drawn from the baseline to the top of
* Chinese, Japanese, and Korean characters.
*
* Available since version: 0.6.0
*/
baselineToCJKTop: number;
/**
* The length of a vertical line drawn from the baseline to the bottom of
* Chinese, Japanese, and Korean characters.
*
* Available since version: 0.6.0
*/
CJKTopToCJKBottom: number;
/**
* The horizontal length of a line drawn from the leftmost pixel of printed
* text to the rightmost pixel of printed text, using the input text to the
* measureText function.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
width: number;
/**
* The maximum amount of vertical space this text will take up, if it were
* printed all on one line.
*
* Available since version: 0.6.0
*/
height: number;
};
};
Font
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { Font } from "@hex-engine/2d";
This Component defines a baseline interface for Font Components, so that other Components can consume fonts without concern for their implementation details.
It is rarely used directly; instead, use BMFont or SystemFont.
FontMetrics
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { FontMetrics } from "@hex-engine/2d";
This Component measures various characters using the specified font in order to provide a function which can accurately predict the render size of text on the page.
It is rarely used directly; instead, use BMFont or SystemFont.
Gamepad
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { Gamepad } from "@hex-engine/2d";
This Component provides the current state of a connected Gamepad, if present.
function Gamepad(
options: Partial<{
/**
* A minimum amount that analog sticks on the gamepad must be pushed from
* the center position before they register as having moved from the center position.
*
* This value can be from 0 to 1, but should usually be a small value, like 0.1.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
deadzone: number;
/**
* An array of button names for the gamepad, cooresponding to the button indices in the
* `gamepad.buttons` array, where `gamepad` is a gamepad returned from `navigator.getGamepads()`.
*
* If you do not provide a list of button names, then names for the buttons on a PlayStation controller
* will be used, even if the connected controller is not a PlayStation controller.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
buttonNames: Array<string>;
/**
* Which gamepad connected to the computer this Gamepad component represents, starting from 0.
*
* Available since version: 0.1.0
*/
gamepadIndex: number;
}>
): {
/**
* A `Vector` indicating which direction the left stick is being pressed in,
* and how far it's being pressed.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
leftStick: Vector;
/**
* A `Vector` indicating which direction the right stick is being pressed in,
* and how far it's being pressed.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
rightStick: Vector;
/**
* A Set containing all the names of the currently pressed buttons.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
pressed: Set<string>;
/**
* A boolean indicating whether a gamepad is connected.
*
* Note that the way the Web Gamepad API works, controllers do not show as connected
* until the user first presses a button.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
present: false;
/**
* The configured deadzone for the gamepad; that is, a number
* used as a minimum value that the analog sticks must be moved
* from their center position before their effective position is
* considered different from the center position.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
deadzone: number;
/**
* The configured button names for the gamepad. These names coorespond to button indices
* in the Web Gamepad API, and will be used in the `pressed` Set.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
buttonNames: Array<string>;
};
Geometry
Available since version: 0.0.1
import { Geometry } from "@hex-engine/2d";
This Component provides information about the shape, position, rotation, and scale
of the current Entity. It is used by useDraw and Physics.Body, among other things.
You should only have one Geometry component per Entity.
function Geometry(init: {
/**
* The shape that the current Entity is.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
shape: Polygon | Circle;
/**
* The position that the current Entity is at.
* If unspecified, it will default to 0, 0.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
position?: Vector | undefined;
/**
* The current rotation of the current Entity,
* expressed in clockwise radians from the x-axis.
*
* If unspecified, it will default to 0.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
rotation?: number | undefined;
/**
* The current x and y scale factor for the current Entity.
* If unspecified, it will default to 1, 1.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
scale?: Vector | undefined;
}): {
/**
* The shape that the current Entity is.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
shape: Polygon | Circle;
/**
* The position that the current Entity is at.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
position: Vector;
/**
* The current rotation of the current Entity,
* expressed in clockwise radians from the x-axis.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
rotation: number;
/**
* The current x and y scale factor for the current Entity.
* If unspecified, it will default to 1, 1.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
scale: Vector;
/**
* A helper function that calculates the position of the current Entity
* relative to the position of the root Entity.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
worldPosition(): Vector;
};
Image
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { Image } from "@hex-engine/2d";
A function that loads and draws an image from a URL.
You can get a URL for an image on disk by importing it, as if it was code:
import myImage from "./my-image.png";
console.log(typeof myImage); // "string"
useNewComponent(() => Image({ url: myImage }));
When you import an image in this way, it will be automatically added to the build and included in the final build output.
function Image(options: {
/**
* The URL where this image can be found.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
url: string;
}): {
/**
* Draw the Image into the provided canvas context, if it has been loaded.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*
* In versions prior to 0.0.1, this method was called `drawIntoContext`
* and had a different signature.
*/
draw(
context: CanvasRenderingContext2D,
options: {
x: number;
y: number;
sourceX?: undefined | number;
sourceY?: undefined | number;
sourceWidth?: undefined | number;
sourceHeight?: undefined | number;
targetWidth?: undefined | number;
targetHeight?: undefined | number;
}
): void;
/**
* Creates a CanvasPattern for the Image, using the provided context.
*
* Available since version: 0.5.3
*
* The primary use of a CanvasPattern is as a fillStyle or strokeStyle on a
* canvas context.
*
* @param context The context you're going to render onto.
* @param repetition Whether to repeat the image, and along which axes. Valid
* values are "repeat", "repeat-x", "repeat-y", or "no-repeat". Defaults to
* "repeat", meaning repeat across both axes.
* @param fallbackStyle A string, CanvasGradient, or CanvasPattern to use as
* a fallback if the image is not yet loaded, or if the pattern cannot be
* created. Defaults to "magenta".
*/
asPattern(
context: CanvasRenderingContext2D,
repetition: "repeat" | "repeat-x" | "repeat-y" | "no-repeat" = "repeat",
fallbackStyle: string | CanvasGradient | CanvasPattern = "magenta"
): string | CanvasGradient | CanvasPattern;
};
ImageFilter
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { ImageFilter } from "@hex-engine/2d";
This Component uses the canvas getImageData and putImageData APIs
to filter the contents of a Canvas by passing it through a filter function.
Note: getImageData and putImageData are very slow, so if you can,
try not to call this every frame.
function ImageFilter(
filter: (data: ImageData) => void
): {
/**
* Reads the pixels in `input` into an ImageData object, passes that `ImageData`
* object into the filter this ImageFilter Component was constructed with,
* and then writes the pixels in the ImageData object into `output`.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
apply(
input: CanvasRenderingContext2D,
output: CanvasRenderingContext2D
): void;
};
Keyboard
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { Keyboard } from "@hex-engine/2d";
This Component provides information about which keys on the user's keyboard are currently pressed.
function Keyboard(
options: {
/**
* If this is set to true, then `event.preventDefault()`
* will be called on every keyboard event that goes through this Component.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
preventDefault?: undefined | boolean;
} = {}
): {
/**
* A Set containing the names of all the keys
* that are currently pressed.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*
* For a list of which Strings will be used, check [This page on MDN](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/KeyboardEvent/key/Key_Values),
* or press some keys and look at the values present
* in this Set using Hex Engine's inspector.
*/
pressed: Set<string>;
/**
* A helper function that creates a `Vector` pointing in the direction indicated by
* the combined state of the four specified direction keys. This is mainly useful
* in that it allows you to treat Gamepad and Keyboard inputs the same.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*
* @param upKey The key that represents "up", eg "w".
* @param downKey The key that represents "down", eg "s".
* @param leftKey The key that represents "left", eg "a".
* @param rightKey The key that represents "right", eg "d".
*/
vectorFromKeys(
upKey: string,
downKey: string,
leftKey: string,
rightKey: string
): Vector;
};
Label
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { Label } from "@hex-engine/2d";
This Component renders some text using the provided Font Component (either a Font, BMFont, or SystemFont).
function Label(options: {
/**
* The text to render.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
text?: string;
/**
* The font to use.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
font: FontImplementation;
}): {
/**
* The amount of space that the text will take up, when drawn.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
size: Vector;
/**
* Draws the text into the context.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*
* In versions prior to 0.0.1, this method was named `drawLabel`,
* and had a different signature.
*/
draw(
context: CanvasRenderingContext2D,
options?: {
x?: number | undefined;
y?: number | undefined;
baseline?: CanvasTextBaseline; // Added in 0.6.0
}
): void;
/**
* The text to render. You can change this to change what to render.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
text: string;
};
LowLevelMouse
Available since version: 0.0.1
import { LowLevelMouse } from "@hex-engine/2d";
A low-level Mouse Component. It provides an interface for mousemove, mousedown, mouseup, mouseover, and mouseout events on the canvas. The positions on these events can be reported either relative to the entity, relative to the world, or relative to the screen, depending on what is desired. Use the positionsRelativeTo option when constructing the component to choose.
For click events, information about whether the cursor is within an Entity's geometry,
and clean separation between left-click, right-click, and middle-click events, use Mouse instead.
If you need to convert an Entity-local position to a world position, you can use the following code snippet:
const worldPoint = useEntityTransforms()
.matrixForWorldPosition()
.transformPoint(localPoint);And if you need to go the other way, you can use the following snippet:
const localPoint = useEntityTransforms()
.matrixForWorldPosition()
.inverse()
.transformPoint(worldPoint);
In versions prior to 0.0.1, this component was called
Mouse.
function LowLevelMouse(options?: {
/**
* Determines what the pos property on the HexMouseEvents from this component should be relative to. Defaults to "owning-entity".
*
* Available since version: 0.7.1
*/
positionsRelativeTo?: "owning-entity" | "world" | "screen";
}): {
/**
* Registers the provided function to be called when the mouse cursor moves.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
onMouseMove: (callback: (event: HexMouseEvent) => void) => void;
/**
* Registers the provided function to be called when any button on the mouse is pressed down.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
onMouseDown: (callback: (event: HexMouseEvent) => void) => void;
/**
* Registers the provided function to be called when any button on the mouse is released.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
onMouseUp: (callback: (event: HexMouseEvent) => void) => void;
/**
* Registers the provided function to be called when the mouse exits the canvas.
*
* Available since version: 0.5.0
*/
onCanvasLeave: (callback: Set<(event: HexMouseEvent) => void>) => {
storage.outCallbacks.add(useCallbackAsCurrent(callback));
},
/**
* Registers the provided function to be called when the mouse enters the canvas.
*
* Available since version: 0.5.0
*/
onCanvasEnter: (callback: Set<(event: HexMouseEvent) => void>) => {
storage.overCallbacks.add(useCallbackAsCurrent(callback));
},
};
Mouse
Available since version: 0.0.1
import { Mouse } from "@hex-engine/2d";
A Component that gives you information about where the Mouse is, relative to the current Entity, and lets you register functions to be called when the mouse cursor interacts with the current Entity.
The Mouse component cooperates with the Geometry component in order to:
- Identify whether the mouse is "inside" the Entity
- Call event listeners with positions relative to the Entity's current position, rotation, and scale
If you do not provide a Mouse component with a specific Geometry component to use when it is created, then it will use Entity.getComponent to obtain one.
If you need to convert an Entity-local position to a world position, you can use the following code snippet:
const worldPoint = useEntityTransforms()
.matrixForWorldPosition()
.transformPoint(localPoint);And if you need to go the other way, you can use the following snippet:
const localPoint = useEntityTransforms()
.matrixForWorldPosition()
.inverse()
.transformPoint(worldPoint);
function Mouse(options?: {
/**
* The entity that this Mouse Component should give information about and relative to.
* If not provided, it will use the current Entity.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
entity?: Entity | undefined;
/**
* The Geometry Component that this Mouse should use to identify whether the cursor
* is inside the Entity or not. If not provided, it will attempt to get a Geometry
* component off of the Entity.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
geometry?: ReturnType<typeof Geometry> | null;
}): {
/**
* A boolean indicating whether the mouse cursor is currently within the Entity, according
* to the Shape on the Geometry this Component has been configured to use.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
isInsideBounds: boolean;
/**
* A boolean indicating whether the left mouse button is currently being pressed.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
isPressingLeft: boolean;
/**
* A boolean indicating whether the right mouse button is currently being pressed.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
isPressingRight: boolean;
/**
* A boolean indicating whether the middle mouse button is currently being pressed.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
isPressingMiddle: boolean;
/**
* The current position of the mouse cursor, relative to the Entity this Component has been
* configured to use.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
position: Vector;
/**
* Registers a function to be called when the mouse cursor enters the configured Entity's bounds.
*
* The function will be called with a `HexMouseEvent`.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
onEnter: (callback: (event: HexMouseEvent) => void) => void;
/**
* Registers a function to be called whenever the mouse cursor moves,
* *even if it is not within the Entity's bounds*.
*
* The function will be called with a `HexMouseEvent`.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
onMove: (callback: (event: HexMouseEvent) => void) => void;
/**
* Registers a function to be called whenever the mouse cursor exits the configured Entity's bounds.
*
* The function will be called with a `HexMouseEvent`.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
onLeave: (callback: (event: HexMouseEvent) => void) => void;
/**
* Registers a function to be called whenever the _LEFT_ mouse button is pressed down
* within the configured Entity's bounds.
*
* If you need an onDown event for a mouse button other than the left button, you will
* have to use the `LowLevelMouse` Component instead.
*
* The function will be called with a `HexMouseEvent`.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
onDown: (callback: (event: HexMouseEvent) => void) => void;
/**
* Registers a function to be called whenever the _LEFT_ mouse button is released
* within the configured Entity's bounds.
*
* If you need an onDown onUp for a mouse button other than the left button, you will
* have to use the `LowLevelMouse` Component instead.
*
* The function will be called with a `HexMouseEvent`.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
onUp: (callback: (event: HexMouseEvent) => void) => void;
/**
* Registers a function to be called whenever the left mouse button is pressed
* and then released within the configured Entity's bounds.
*
* The function will be called with a `HexMouseEvent`.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
onClick: (callback: (event: HexMouseEvent) => void) => void;
/**
* Registers a function to be called whenever the right mouse button is pressed
* and then released within the configured Entity's bounds.
*
* The function will be called with a `HexMouseEvent`.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
onRightClick: (callback: (event: HexMouseEvent) => void) => void;
/**
* Registers a function to be called whenever the middle mouse button is pressed
* and then released within the configured Entity's bounds.
*
* The function will be called with a `HexMouseEvent`.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
onMiddleClick: (callback: (event: HexMouseEvent) => void) => void;
};
Ogmo.Project
Available since version: 0.4.1
import { Ogmo, useNewComponent } from "@hex-engine/2d";
import myProject from "./myProject.ogmo";
useNewComponent(() => Ogmo.Project(myProject));
A Component that provides an interface for working with an Ogmo Editor project.
Note: Several of the types in this overview are omitted. Rely on your IDE for definitions of these types.
function OgmoProject(
/**
* The imported *.ogmo file
*
* Available since version: 0.4.1
*/
projectData: any,
/**
* An object map of functions that will be used to
* construct entities in Ogmo levels, by name; for example:
*
* { player: (entData) => useChild(() => Player(entData)) }
*
* Available since version: 0.4.1
* Changed to receive Ogmo.EntityFactoryInfo in version: 0.9.0
*/
entityFactories: {
[name: string]: (info: Ogmo.EntityFactoryInfo) => Entity;
} = {},
/**
* An optional function that will be called to construct entities for decals.
* The default implementation uses Ogmo.Decal.
*
* Available since version: 0.4.1
* Changed to receive Ogmo.DecalFactoryInfo in version: 0.9.0
*/
decalFactory?: (info: Ogmo.DecalFactoryInfo) => Entity
): {
/**
* All of the tilesets specified in the Ogmo project.
*
* Available since version: 0.4.1
*/
tilesets: Array<OgmoTileset>;
/**
* All of the layer definitions specified in the Ogmo project.
*
* Available since version: 0.4.1
*/
layers: Array<OgmoProjectLayer>;
/**
* Create a new OgmoLevel component for the given level data,
* and add it to the current component's Entity.
*
* ```ts
* import levelData from "./level.json";
* ogmo.useLevel(levelData);
* ```
*
* You may pass a component function as the second argument
* to override the component used to render the level's tile
* layers. By default, Ogmo.TileRenderer is used.
*
* Available since version: 0.4.1. tileRenderer parameter added in 0.8.0.
*/
useLevel(
levelData: any,
tileRenderer?: (layer: LevelTileLayer, levelData: any) => any
): Component & {
/**
* The size of the level, in pixels.
*
* Available since version: 0.4.1
*/
size: Vector;
/**
* The render offset for the level.
*
* Available since version: 0.4.1
*/
offset: Vector;
/**
* Any custom values that were placed on the level from the Ogmo editor.
*
* Available since version: 0.4.1
*/
values: { [key: string]: any };
/**
* An array of the layers in the level.
*
* Available since version: 0.4.1
*/
layers: Array<OgmoLevelLayer>;
};
};
Ogmo.Level
Available since version: 0.4.1
import { Ogmo } from "@hex-engine/2d";
Ogmo.Level;
A component representing a single Ogmo level. When created, it will loop over all the layers, decals, tiles, entities, and grids in the level, and create appropriate objects to represent each.
It cooperates with an Ogmo.Project component to get layer information and create entities and decals.
You cannot create these manually; instead, use the useLevel method on Ogmo.Project.
Ogmo.Decal
Available since version: 0.4.1
import { Ogmo } from "@hex-engine/2d";
Ogmo.Decal;
The default Ogmo decal component, used in the creation of decal entities when rendering the decal layer of an Ogmo level.
It loads the image for the decal, and draws it with the position, rotation, and scale specified by the decal data in the level.
If you want to use a different component to render decals, instead of this
one, then you can override it when you create the Ogmo.Project by passing
a custom function as its decalFactory parameter.
Ogmo.TileRenderer
Available since version: 0.8.0
import { Ogmo } from "@hex-engine/2d";
Ogmo.TileRenderer;
The default Ogmo tile renderer component, used to draw the tile layers of an Ogmo level.
It uses Ogmo.TileLayerParser to create a TileMap for the layer, then draws the layer offset such that its center will be at 0, 0.
If you want to use a different component to render tile layers, instead of this
one, then you can override it when you call Ogmo.Project's
useLevel method by passing a component function as its tileRenderer
parameter.
Ogmo.TileLayerParser
Available since version: 0.8.0
import { Ogmo } from "@hex-engine/2d";
Ogmo.TileLayerParser;
A component that creates a TileMap component for a tile layer from
an Ogmo level.
This component is used by Ogmo.TileRenderer which is the default
implementation for rendering tile layers from Ogmo levels. You may find
Ogmo.TileLayerParser useful if you are overriding the default TileRenderer
with a different implementation. To override it, pass a component function
to Ogmo.Project's useLevel method as its tileRenderer parameter.
Physics.Engine
Available since version: 0.0.1
import { Physics } from "@hex-engine/2d";
Physics.Engine;
A Component that should be placed on the root Entity if you want to use physics in your game.
Hex Engine's Physics are provided by Matter.js.
function PhysicsEngine(options?: {
/**
* Whether to render red wireframes of all physics bodies and constraints
* into the canvas, for debugging purposes.
*
* Defaults to false.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
debugDraw?: boolean;
/**
* The gravity of the world, as a Vector with x and y Components.
* An x or y value of 1 means "normal Earth gravity in this direction".
*
* Defaults to new Vector(0, 1).
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
gravity?: Vector;
/**
* Whether to enable sleeping in the physics simulation.
* This puts bodies that have not moved in a while to "sleep", and does
* not update them until another body collides with them. This helps with framerate,
* but at the expense of simulation accuracy.
*
* Defaults to true.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
enableSleeping?: boolean;
}): {
/**
* The Matter.js Engine object.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
engine: Matter.Engine;
/**
* Adds a collision listener for the current Entity.
*
* It will be called when another Entity's Physics.Body
* starts and stops colliding with this Entity's.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
addCollisionListener: (
callback: (other: {
/**
* Whether this is a "collisionStart" or "collisionEnd" event;
* in other words, whether the current Entity just started touching
* something, or just finished touching something.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.3
*
* In versions prior to 0.0.3, only "collisionStart" events were reported.
*/
kind: "start" | "end";
/**
* The other body that the current Entity's physics body collided with.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
body: Matter.Body;
/**
* If the other body that the current Entity collided with belonged to
* an Entity, then this is the Entity that the current Entity collided with.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
entity: null | Entity;
}) => void
) => void;
/**
* Whether to render red wireframes of all physics bodies and constraints
* into the canvas, for debugging purposes.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
debugDraw: boolean;
};
Physics.Body
Available since version: 0.0.1
import { Physics } from "@hex-engine/2d";
Physics.Body;
A Component that should be added to any Entity that will participate in the physics simulation.
Hex Engine's Physics are provided by Matter.js.
function PhysicsBody(
geometry: ReturnType<typeof Geometry>,
options?: Partial<{
/**
* A label for this body, for debugging purposes.
* If unspecified, defaults to the current Entity's name.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
label: string;
/**
* Whether the body should *not* move around.
* If this is set, things will still collide with it, but it'll be "frozen" in the sky.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
isStatic: boolean;
/**
* The density of this body.
*
* For more information, check the [Matter.js documentation](https://brm.io/matter-js/docs/classes/Body.html).
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
density: number;
/**
* The friction of this body.
*
* For more information, check the [Matter.js documentation](https://brm.io/matter-js/docs/classes/Body.html).
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
friction: number;
/**
* The friction this body feel in the air, due to air resistance.
*
* For more information, check the [Matter.js documentation](https://brm.io/matter-js/docs/classes/Body.html).
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
frictionAir: number;
/**
* Whether this body is a "Sensor"; if it is, then it will emit collision
* events, but it will be frozen in space and objects will go right through it.
*
* In some engines, these are called "Brushes" or "Volumes".
*
* For more information, check the [Matter.js documentation](https://brm.io/matter-js/docs/classes/Body.html).
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
isSensor: boolean;
/**
* How bouncy this body is.
*
* For more information, check the [Matter.js documentation](https://brm.io/matter-js/docs/classes/Body.html).
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
restitution: number;
/**
* The time scale that this body runs through the simulation at.
*
* For more information, check the [Matter.js documentation](https://brm.io/matter-js/docs/classes/Body.html).
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
timeScale: number;
/**
* The static friction of the body (in the Coulomb friction model).
*
* For more information, check the [Matter.js documentation](https://brm.io/matter-js/docs/classes/Body.html).
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
frictionStatic: number;
/**
* Properties that define whether this body collides with other bodies.
*
* For more information, check the [Matter.js documentation](https://brm.io/matter-js/docs/classes/Body.html).
*
* Available since version: 0.1.0
*/
collisionFilter: {
group: number;
category: number;
mask: number;
};
}>
): {
/**
* The created Matter.Body.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
body: Matter.Body;
/**
* Apply the specified force to the specified position on the physics body.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
applyForce(position: Vector, force: Vector): void;
/**
* Sets the angle of the physics body.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
setAngle(angle: number): void;
/**
* Sets the angular velocity of the physics body; how fast it is rotating.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
setAngularVelocity(velocity: number): void;
/**
* Sets the density of the physics body.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
setDensity(density: number): void;
/**
* Sets the moment of inertia for the physics body.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
setInertia(inertia: number): void;
/**
* Sets the mass of the physics body.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
setMass(mass: number): void;
/**
* Sets the position of the physics body.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
setPosition(position: Vector): void;
/**
* Sets whether the physics body is "static".
*
* If this is set to true, things will still collide with the body,
* but it'll be "frozen" in the sky.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
setStatic(isStatic: boolean): void;
/**
* Sets the directional velocity of the physics body, in the specified x and y directions.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
setVelocity(velocity: Vector): void;
/**
* Registers a function to be run when the physics body collides with
* another physics body.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
onCollision: (
callback: (other: {
/**
* Whether this is a "collisionStart" or "collisionEnd" event;
* in other words, whether the current Entity just started touching
* something, or just finished touching something.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.3
*
* In versions prior to 0.0.3, only "collisionStart" events were reported.
*/
kind: "start" | "end";
/**
* The other body that the current Entity's physics body collided with.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
body: Matter.Body;
/**
* If the other body that the current Entity collided with belonged to
* an Entity, then this is the Entity that the current Entity collided with.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
entity: null | Entity;
}) => void
) => void;
) => void;
};
Physics.Constraint
Available since version: 0.0.1
import { Physics } from "@hex-engine/2d";
Physics.Constraint;
A Component that can be used to bind two physics bodies together with a rope, spring, nail, or other real or imaginary constraint.
Hex Engine's Physics are provided by Matter.js.
function PhysicsConstraint(
options: Partial<{
/**
* A value from 0 to 1 that determines how quickly the constraint returns
* to its resting length. 1 means very stiff, and 0.2 means a soft spring.
*
* For more information, check the [Matter.js Documentation](https://brm.io/matter-js/docs/classes/Constraint.html)
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
stiffness: number;
/**
* A value from 0 to 1 that determines the damping, which limits oscillation.
*
* 0 means no damping, and 0.1 means no damping.
*
* For more information, check the [Matter.js Documentation](https://brm.io/matter-js/docs/classes/Constraint.html)
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
damping: number;
/**
* The first body that this constraint is attached to.
*
* For more information, check the [Matter.js Documentation](https://brm.io/matter-js/docs/classes/Constraint.html)
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
bodyA: Matter.Body;
/**
* The second body that this constraint is attached to.
*
* For more information, check the [Matter.js Documentation](https://brm.io/matter-js/docs/classes/Constraint.html)
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
bodyB: Matter.Body;
/**
* The position where the constraint is attached to `bodyA`, or a world-space position
* that the constraint is attached to if `bodyA` is not defined..
*
* For more information, check the [Matter.js Documentation](https://brm.io/matter-js/docs/classes/Constraint.html)
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
pointA: Vector;
/**
* The position where the constraint is attached to `bodyB`, or a world-space position
* that the constraint is attached to if `bodyB` is not defined..
*
* For more information, check the [Matter.js Documentation](https://brm.io/matter-js/docs/classes/Constraint.html)
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
pointB: Vector;
/**
* The resting length of the constraint.
*
* For more information, check the [Matter.js Documentation](https://brm.io/matter-js/docs/classes/Constraint.html)
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
length: number;
/**
* A label, for debugging purposes.
*
* For more information, check the [Matter.js Documentation](https://brm.io/matter-js/docs/classes/Constraint.html)
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
label: string;
}>
): {
/**
* The created Matter constraint.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
constraint: Matter.Constraint;
};
ProceduralSfx
Available since version: 0.0.1
import { ProceduralSfx } from "@hex-engine/2d";
A Component that can be used to generate procedural sound effects, by synthesizing modal sounds. A modal sound is a resonating, ringing sound that is composed out of several different sine waves, such as the sound that is emitted when you strike a wine glass or metal rod.
If you use a spectrogram to identify the frequency, amplitude, and decay rate of the sine waves that the sound is made out of, then you can provide them to this function, and it will create a model that synthesizes that sound.
If you then vary the frequency, amplitude, or decay rate slightly each time the sound is played, you can get a rich bank of sound effects all from one sound.
function ProceduralSfx(
modes: Array<{
frequency: number;
amplitude: number;
decay: number;
}>
): {
/**
* Returns the synthesis model, if it is available.
*
* To work around browsers disallowing sound to be played without the user interacting with
* the page first, the synthesis model will not be created until the first time the user
* clicks on the page, or presses a key. Until then, this will be `null`.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
synthesis: Object; // return type of makeModalSynthesis from the "modal-synthesis" package
/**
* Plays the sound, if the browser is allowed to play sound; browser disallow
* webpages from playing sound until the first time the user interacts with the
* page (via a click or keypress). So this method won't have an effect until after
* the first time the user has clicked somewhere on the page, or pressed some key
* on their keyboard.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
play(options?: {
amplitudeMultiplier?: number | ((modeIndex: number) => number) | undefined;
frequencyMultiplier?: number | ((modeIndex: number) => number) | undefined;
decayMultiplier?: number | ((modeIndex: number) => number) | undefined;
whiteNoiseDuration?: number | undefined;
}): void;
};
SpriteSheet
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { SpriteSheet } from "@hex-engine/2d";
A Component that helps you draw individual sprites from a sprite sheet.
It is designed to be used with an image that is laid out like a film strip, with many sprites on it. Each sprite will be assigned an index from left-to-right, top-to-bottom (if there are multiple rows in the sheet), and you can specify which index should be drawn to the canvas.
function SpriteSheet(options: {
/**
* The image URL.
*
* You can get a URL for an image on disk by `import`ing it, as if it was code:
*
* ```ts
* import myImage from "./my-image.png";
*
* console.log(typeof myImage); // "string"
* ```
*
* When you import an image in this way, it will be automatically
* added to the build and included in the final build output.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
url: string;
/**
* The width of each "tile" in the sheet, in pixels.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
tileWidth: number;
/**
* The height of each "tile" in the sheet, in pixels.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
tileHeight: number;
}): {
/**
* The size of each tile in the sheet.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
tileSize: Vector;
/**
* Draw the tile at the specified index into the canvas.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*
* In versions prior to 0.0.1, this method was named `drawSpriteIntoContext`,
* and had a different signature.
*/
draw(
context: CanvasRenderingContext2D,
options: {
x?: number | void;
y?: number | void;
tileIndex: number;
width?: void | number;
height?: void | number;
}
): void;
};
SystemFont
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { SystemFont } from "@hex-engine/2d";
This Component uses an installed font on the system to render text into the canvas.
function SystemFont(options: {
/**
* The CSS name of the font; eg "sans-serif" or "Arial".
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
name: string;
/**
* The size of the font, in pixels.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
size: number;
/**
* The CSS color of the text that this font draws,
* eg "red" or "#ff0000" or "rgba(255, 0, 0, 0)".
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
color?: void | string;
}): {
name: string;
size: number;
color: string;
/**
* Whether the font is ready to be drawn to the canvas yet.
* This is provided for compatibility with the general `Font`
* interface, but for SystemFont, it always returns true.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
readyToDraw(): void;
/**
* Measures how many pixels wide the specified text would be,
* if it was rendered using this font.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
measureWidth(text: string): number;
/**
* Returns this font's size.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
getFontSize(): number;
/**
* Draws some text into the canvas, using this font.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*
* In versions prior to 0.0.1, this method had a different signature.
*/
drawText(
context: CanvasRenderingContext2D,
text: string,
options?: {
x?: number | undefined;
y?: number | undefined;
baseline?: CanvasTextBaseline | undefined; // Added in version 0.6.0.
}
): void;
/**
* Measure the sizes of various aspects of this font.
* See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Typeface#Font_metrics
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
* Return value shape changed in version: 0.6.0
*/
measureText: (
text: string
) => {
/**
* The length of a vertical line drawn from the baseline to the mean line.
*
* In layman's terms: the height of lowercase letters like a, e, x, o, etc.
*
* Available since version: 0.6.0
*/
baselineToMeanLine: number;
/**
* The length of a vertical line drawn from the baseline to the cap line.
*
* In layman's terms: the height of uppercase letters.
*
* Available since version: 0.6.0
*/
baselineToCapLine: number;
/**
* The length of a vertical line drawn from the baseline to the descent line.
*
* In layman's terms: the height of the little tails that hang off the
* bottom of the baseline in lowercase letters like q, p, y, j, g, etc.
*
* Available since version: 0.6.0
*/
baselineToDescentLine: number;
/**
* The length of a vertical line drawn from the baseline to the ascent line.
*
* In layman's terms: the height of "tall" lowercase letters, like l, f, etc.
*
* Available since version: 0.6.0
*/
baselineToAscentLine: number;
/**
* The length of a vertical line drawn from the descent line to the ascent line.
*
* Available since version: 0.6.0
*/
descentLineToAscentLine: number;
/**
* The length of a vertical line drawn from the baseline to the bottom of
* Chinese, Japanese, and Korean characters.
*
* Available since version: 0.6.0
*/
baselineToCJKBottom: number;
/**
* The length of a vertical line drawn from the baseline to the top of
* Chinese, Japanese, and Korean characters.
*
* Available since version: 0.6.0
*/
baselineToCJKTop: number;
/**
* The length of a vertical line drawn from the baseline to the bottom of
* Chinese, Japanese, and Korean characters.
*
* Available since version: 0.6.0
*/
CJKTopToCJKBottom: number;
/**
* The horizontal length of a line drawn from the leftmost pixel of printed
* text to the rightmost pixel of printed text, using the input text to the
* measureText function.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
width: number;
/**
* The maximum amount of vertical space this text will take up, if it were
* printed all on one line.
*
* Available since version: 0.6.0
*/
height: number;
};
};
TextBox
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { TextBox } from "@hex-engine/2d";
This Component lays out text in lines, fitting as many words as it can on one line before continue onto the next. When you use it, it tells you which lines it rendered, and which parts of the text you provided didn't fit into the text box (if any). You can use this information to re-render the text box with new content, once the user has read the text.
export default function TextBox(options: {
/**
* The font to use to draw text in this text box.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
font: ReturnType<typeof Font | typeof BMFont | typeof SystemFont>,
/**
* The size of the text box.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
size: Vector,
/**
* The number of vertical pixels to allocate to each line of text.
*
* If unspecified, it defaults to the height of the text from the baseline to the
* ascent, plus double the height of the text from the baseline to the descender.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
lineHeight?: number,
}: {
/**
* Draws as much of the provided text as will fit into the text box,
* and returns information how much of the text fit.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*
* In versions prior to 0.0.1, this method had a different signature.
*/
drawText(
context: CanvasRenderingContext2D,
text: string,
location?: {
x?: number;
y?: number;
baseline?: CanvasTextBaseline | undefined; // Added in version 0.6.0.
}
): {
/**
* A boolean indicating whether all the text that was provided fit into the textbox.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
didTextFit: boolean;
/**
* A string containing any remaining text that didn't fit into the box.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
remainingText: string;
/**
* An Array containing all the lines that were printed.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
printedLines: Array<string>,
}
}
Tiled.Tileset
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { Tiled } from "@hex-engine/2d";
import someTileset from "./someTileset.xml";
Tiled.Tileset(someTileset);
This Component loads data from a Tiled XML tileset file and creates a SpriteSheet Component out of it.
function Tileset(
data: XMLSourceLoader.Element
): {
/**
* The created SpriteSheet component.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
spriteSheet: ReturnType<typeof SpriteSheet>;
};
Tiled.Layer
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { Tiled } from "@hex-engine/2d";
Tiled.Layer;
This Component represents the data for a single layer within a Tiled map XML file.
You'll rarely create it directly; instead, you'll get it from a Tiled.Map.
function Layer(
layer: XMLSourceLoader.Element
): {
/**
* A grid containing numbers that map to the indices of the tiles
* as found in the Tileset SpriteSheet.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
grid: Grid<number>;
/**
* A boolean indicating whether this layer is visible.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
visible: boolean;
};
Tiled.Map
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { Tiled } from "@hex-engine/2d";
import someMap from "./someMap.xml";
Tiled.Map(someMap);
This Component loads data from a Tiled map XML file and creates SpriteSheet and TileMap Components that you can use to draw the map into the canvas.
function TiledMap(
data: XMLSourceLoader.Element
): {
/**
* The tileset used by the map.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
tileset: ReturnType<typeof Tiled.Tileset>;
/**
* An Array of Tiled.Layer Compponents,
* each corresponding to a layer in the Tiled map.
*
* Available since version: 0.1.0
*/
layers: Array<ReturnType<typeof Tiled.Layer>>;
/**
* An Array of TileMap Components,
* each corresponding to a *visible* layer in the Tiled map.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
tileMaps: Array<ReturnType<typeof TileMap>>;
/**
* The size of the map, in tiles.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
sizeInTiles: Vector;
/**
* The size of the map, in pixels.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
sizeInPixels: Vector;
/**
* The size of a single tile in the map.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
tileSize: Vector;
/**
* All the objects that were present in the map, for you to use however you like.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.0
*/
objects: Array<
| {
kind: "string";
object: string;
}
| {
kind: "unknown";
object: XMLSourceLoader.Element;
id: string;
name: string;
location: Vector;
size?: Vector;
properties: Array<{
name: string;
value: string;
type: "bool" | "color" | "float" | "file" | "int" | "string";
}>;
}
| {
kind: "point";
object: XMLSourceLoader.Element;
id: string;
name: string;
location: Vector;
size?: Vector;
properties: Array<{
name: string;
value: string;
type: "bool" | "color" | "float" | "file" | "int" | "string";
}>;
}
| {
kind: "ellipse";
object: XMLSourceLoader.Element;
id: string;
name: string;
location: Vector;
size?: Vector;
properties: Array<{
name: string;
value: string;
type: "bool" | "color" | "float" | "file" | "int" | "string";
}>;
}
| {
kind: "text";
object: XMLSourceLoader.Element;
id: string;
name: string;
location: Vector;
size?: Vector;
properties: Array<{
name: string;
value: string;
type: "bool" | "color" | "float" | "file" | "int" | "string";
}>;
}
| {
kind: "polygon";
points: Array<Vector>;
object: XMLSourceLoader.Element;
id: string;
name: string;
location: Vector;
size?: Vector;
properties: Array<{
name: string;
value: string;
type: "bool" | "color" | "float" | "file" | "int" | "string";
}>;
}
>;
};
TileMap
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { TileMap } from "@hex-engine/2d";
This Component uses a Grid of tile indices and a SpriteSheet Component to draw a large map of tiles to the canvas.
function TileMap(
sheet: ReturnType<typeof SpriteSheet>,
grid: Grid<number>
): {
/**
* Draws all the tiles in this map into the canvas.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*
* In versions prior to 0.0.1, this method was called `drawMapIntoContext`, and had a different signature.
*/
draw(
context: CanvasRenderingContext2D,
position?: {
x?: number | void;
y?: number | void;
} = {}
): void;
};
Timer
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { Timer } from "@hex-engine/2d";
This Component can be used to check how far the current time is from some desired time in the future.
function Timer(): {
/**
* Sets the timer's internal "target" time to some time in the future.
*
* If you never call setToTimeFromNow, the target time of the timer will be
* the time that the timer was created.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
setToTimeFromNow(msFromNow: number): void;
/**
* Returns how many milliseconds away the current time is from the target time.
*
* If the target time has not yet been reached, this number will be negative.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
distanceFromSetTime(): number;
/**
* Returns a boolean indicating whether the target time set by `setToTimeFromNow`
* has been reached.
*
* Available since version: 0.0.1
*/
hasReachedSetTime(): boolean;
};
Hooks
@hex-engine/2d comes with several hook functions you can use within your own Component functions.
useContext
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { useContext } from "@hex-engine/2d";
useContext(): CanvasRenderingContext2D
Returns the 2d rendering context of the root component's Canvas.
This is the same context that gets passed into useDraw's callback.
useDraw
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { useDraw } from "@hex-engine/2d";
export default function useDraw(onDraw: (context: CanvasRenderingContext2D) => void, { roundToNearestPixel: boolean }?): void
Register a function to be called once per frame, after all useUpdate functions have been called.
The function will receive a 2d canvas context it can draw into.
The context you receive will already be rotated and translated such that position 0, 0 is the upper-left corner of the current Entity, so in most cases, you will not need to worry about x/y positioning.
useUpdate
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { useUpdate } from "@hex-engine/2d";
useUpdate(callback: (delta: number) => void): void
Registers a function to be called once every frame, prior to drawing.
The function will receive a single argument, delta, which is the number of milliseconds
that have passed since the last frame was rendered.
useEntitiesAtPoint
Available since version: 0.0.1
import { useEntitiesAtPoint } from "@hex-engine/2d";
useEntitiesAtPoint(worldPos: Vector): Array<Entity>
Get all the entities at the given world position, sorted by reverse draw order, such that one that gets drawn last (and is therefore on top) is the first in the array.
useEntityTransforms
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { useEntityTransforms } from "@hex-engine/2d";
useEntityTransforms(entity?: Entity): { matrixForWorldPosition: () => TransformMatrix, matrixForDrawPosition: () => TransformMatrix }
Get the matrix transforms for the specified Entity, or the current Entity if no entity is provided.
useFilledPixelBounds
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { useFilledPixelBounds } from "@hex-engine/2d";
useFilledPixelBounds(context: CanvasRenderingContext2D): { minX: number; maxX: number; minY: number; maxY: number; }
Searches through the provided canvas context for non-transparent pixels and identifies a bounding box that contains them.
Warning: This function is expensive. Avoid using it on every frame.
useInspectorHoverOutline
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { useInspectorHoverOutline } from "@hex-engine/2d";
useInspectorHoverOutline(getShape: () => Polygon | Circle)
Sets up the Inspector so that when the current Entity or Component is hovered over, the provided function will be called to get a shape that should be drawn onto the screen.
This function does nothing in release builds.
useInspectorSelectEntity
Available since version: 0.3.2
import { useInspectorSelectEntity } from "@hex-engine/2d";
useInspectorSelectEntity(getGeometry: () => Geometry)
Sets up the Inspector to enable hovering and clicking on the current rendered Entity by calling the provided function to get a Geometry for the Entity. Only rendered Entities that use a Geometry component can be hovered/clicked on when the Inspector is in entity select mode.
This function does nothing in release builds.
useRawDraw
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { useRawDraw } from "@hex-engine/2d";
useRawDraw(callback: (context: CanvasRenderingContext2D): void
Registers a function to be called once a frame, after all useUpdate functions have been called.
Unlike useDraw, useRawDraw does not transform the context by the current Entity's matrix transform.
In most cases, you should use useDraw instead of useRawDraw.
useDebugOverlayDrawTime
Available since version: 0.0.1
import { useDebugOverlayDrawTime } from "@hex-engine/2d";
useDebugOverlayDrawTime(): void
This hook specifies to the default draw order sort function that this Component's draw callbacks should be drawn last, after everything else, because this component renders debug overlay(s) that should be drawn on top of everything else.
If you are using a custom draw order sort and want to preserve this functionality,
you can use the Canvas.DrawOrder.isDebugOverlay function to identify Components
that have called this hook.
useCanvasDrawOrderSort
Available since version: 0.0.1
import { useCanvasDrawOrderSort } from "@hex-engine/2d";
This component will check the root Entity for a Canvas.DrawOrder component, and if it is present, it will return its sort function. Otherwise, it returns Canvas.DrawOrder.defaultSort.
useFirstClick
Available since version: 0.0.1
import { useFirstClick } from "@hex-engine/2d";
useFirstClick(handler: () => void): void
This function will run the provided function the first time a mouse click occurs.
Note that it only works if there is at least one Mouse or LowLevelMouse Component
loaded in your game when the first click occurs. To be on the safe side, you should
probably also add a LowLevelMouse or Mouse Component to the Component that calls useFirstClick.
useFirstKey
Available since version: 0.0.1
import { useFirstKey } from "@hex-engine/2d";
useFirstKey(handler: () => void): void
This function will run the provided function the first time a key is pressed.
Note that it only works if there is at least one Keyboard Component loaded in
your game when the first keypress occurs. To be on the safe side, you should
probably also add a Keyboard Component to the Component that calls useFirstKey.
useAudioContext
Available since version: 0.0.1
import { useAudioContext } from "@hex-engine/2d";
useAudioContext(): AudioContext | null
Retrieve the current AudioContext from the root Entity's AudioContext component, if any.
useCanvasSize
Available since version: 0.1.15
import { useCanvasSize } from "@hex-engine/2d";
useCanvasSize(): Object
Returns an object with three properties on it:
canvasSize: Vector: A Vector that will get mutated such that it always equals the current canvas sizeonCanvasResize(() => void): void: A function that lets you register a function to be run every time the canvas size changes.resizeCanvas: ({ realWidth: number | string, realHeight: number| string, pixelWidth: number, pixelHeight: number }) => void: A function that resizes the canvas.
useWindowSize
Available since version: 0.1.15
import { useWindowSize } from "@hex-engine/2d";
useWindowSize(): Object
Returns an object with two properties on it:
windowSize: ReadOnlyVector: A Vector that will get mutated such that it always equals the window size (so you shouldn't mutate it)onWindowResize(() => void): void: A function that lets you register a function to be run every time the window size changes.
Other
Preloader
Available since version: 0.0.0
import { Preloader } from "@hex-engine/2d";
An object that helps ensure used resources are loaded before they are used.
When resources that must be fetched over the network are created (such as Images and Audio),
they register themselves with thie Preloader. To wait until all registered resources have been
loaded, use Preloader.load().then(() => {}).
Methods
addTask
Available since version: 0.0.0
addTask(task: () => Promise<any>): void
Adds a new task to the Preloader. It will start running immediately.
load
Available since version: 0.0.0
load(): Promise<void>
Returns a Promise which does not resolve until all tasks that have been added to the Preloader have resolved.